Artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly integrated into various sectors, with healthcare being one of the most impactful. This report explores the applications, benefits, and challenges of AI in medicine.
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone in the transformation of various industries, with the healthcare sector experiencing some of the most significant impacts. This report delves into the multifaceted role of AI in medicine, examining its applications, benefits, and the challenges it poses.
data source: Zoológico Santa Fe data lab
Applications of AI in Medicine
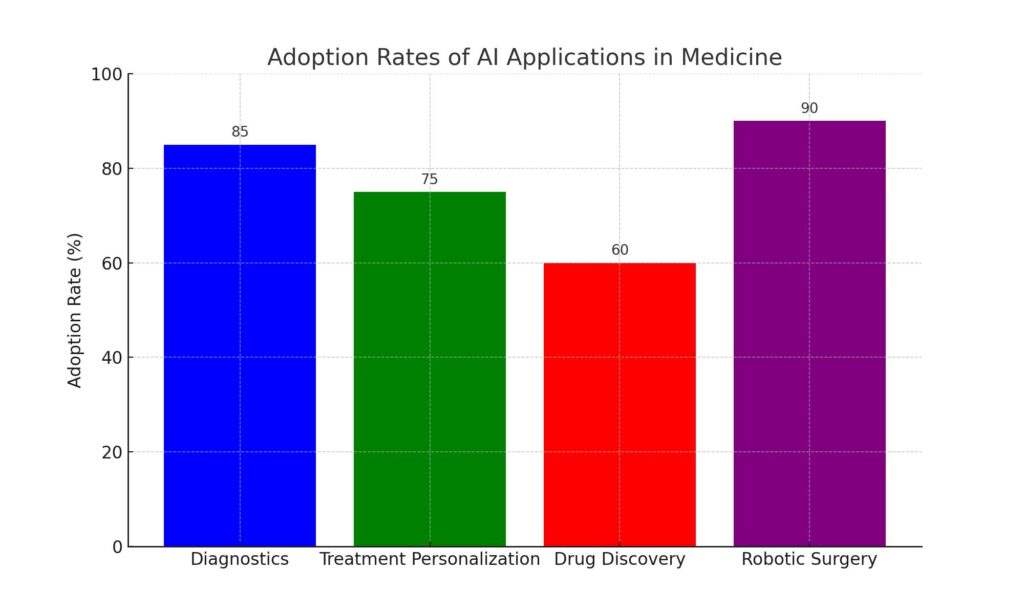
- Diagnostics: AI technologies, particularly machine learning algorithms, are revolutionizing medical diagnostics. These systems analyze imaging data such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with higher accuracy and speed than traditional methods, leading to faster and more reliable diagnoses.
- Treatment Personalization: Personalized medicine, tailored to individual patient profiles, is becoming a reality with AI. Predictive models analyze patient data to forecast responses to various treatment regimens, optimizing therapeutic effectiveness and reducing adverse effects.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the drug development process by simulating the effects of compounds and predicting the behavior of molecules. This not only speeds up the discovery phase but also enhances the likelihood of identifying viable new drugs.
- Robotic Surgery: Surgical robots, equipped with AI, are being increasingly deployed in operating rooms. These robots assist surgeons in performing precise and minimally invasive surgeries, enhancing outcomes and reducing recovery times for patients.

Benefits of AI in Medicine
- Increased Efficiency: AI streamlines healthcare processes, from patient intake to diagnosis and treatment, significantly cutting down the time and costs associated with traditional healthcare delivery.
- Improved Accuracy: By reducing human error in tasks such as diagnosing and prescribing, AI improves the accuracy and reliability of healthcare services.
- Enhanced Accessibility: AI-powered telemedicine and mobile applications extend healthcare’s reach, especially in remote and underserved areas, ensuring more people have access to quality medical advice and interventions.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Medicine
- Data Privacy: The use of AI in healthcare raises significant privacy concerns, as handling sensitive patient data necessitates stringent security measures to prevent breaches and misuse.
- Ethical Considerations: AI’s decision-making processes must be transparent and understandable to ensure they adhere to ethical medical practices and maintain patient trust.
- Integration Issues: Merging AI with existing healthcare infrastructures presents logistical, financial, and technical challenges. It requires substantial investment in technology and training for healthcare professionals.
| AI Application | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | 85 |
| Treatment Personalization | 75 |
| Drug Discovery | 60 |
| Robotics in Surgery | 90 |
Conclusion
The integration of AI into medicine is poised to redefine traditional practices and promises substantial improvements in patient care and operational efficiency. However, to fully harness the benefits of AI, the healthcare industry must navigate the accompanying ethical and logistical challenges. Careful implementation and continued oversight are essential to ensure AI tools are used responsibly and effectively.
